USMA Help
Usher Syndrome Missense Analysis
The Help is presented here as a slide show using s5.
Click here to display a plain page.
Use the arrows of your keyboard to move into the slide show.
Mouse control is also available at the bottom-right corner of the page.
David Baux
CHU-Montpellier
What is USMA?
- Usher Syndrome Missense Analysis
- A software, Website dedicated to the in silico analysis of missense variants,
- related to 9 Usher proteins.
- It uses specific pieces of information,
- alignments, annotations, 3D structures...
- Manually curated.
What is USMA?
USMA is divided into four main parts:
- Otholog alignments
- Domain alignments
- Secondary structure
- 3D structure
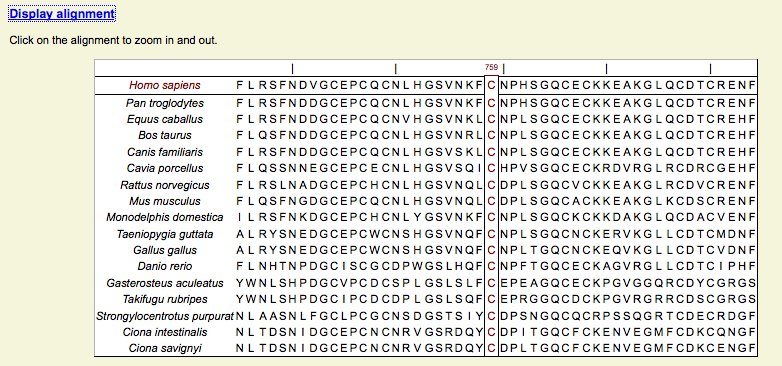
Ortholog analysis - Alignment
Conservation of the residue is assessed within a set of ortholog sequences (i.e. the same protein in different species).
Specific features (often unique):
- Window display of the alignement, with a zoom function
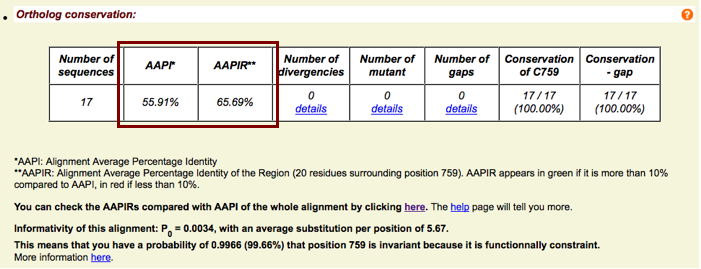
Ortholog analysis - AAPI(R)
- AAPI & AAPIR
- Alignment Average Percentage Identity (of the Region)
- Mean conservation of the whole alignement or of a window of 20 residues (Region)
- Available for the position of interest
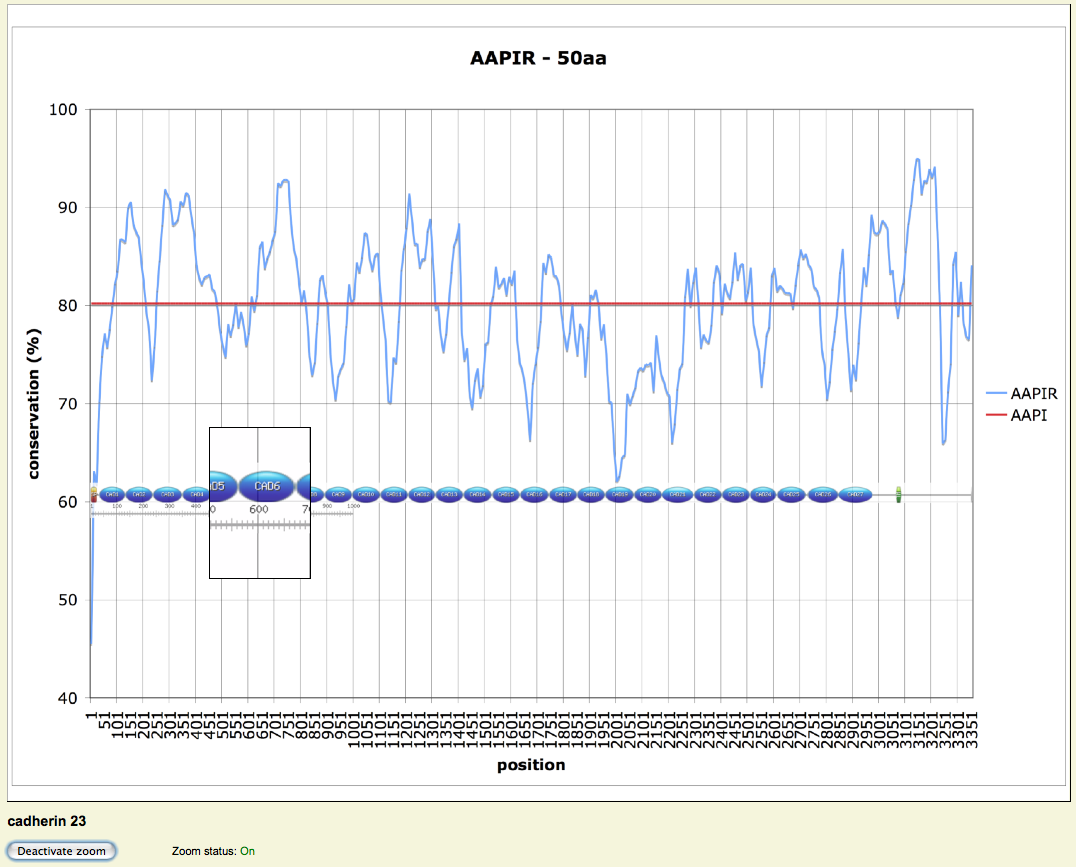
Ortholog analysis - AAPI(R)
- AAPIRs have also been calculated for the whole alignments
- Window size & positions depends on the size of the protein
- Highlights highly and poorly conserved regions
- Results have been plotted with AAPI and scaled protein pictures (zoom function)
Ortholog analysis - AAPI(R)
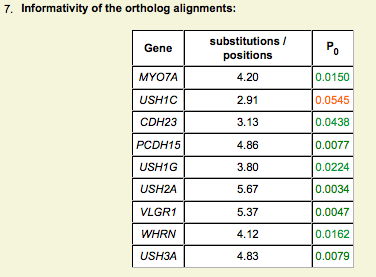
Ortholog analysis - Informativity
- P0 calculated from Greenblatt et al., 2003
- 1-P0 indicates the probability that a invariant position is actually functionally constrained
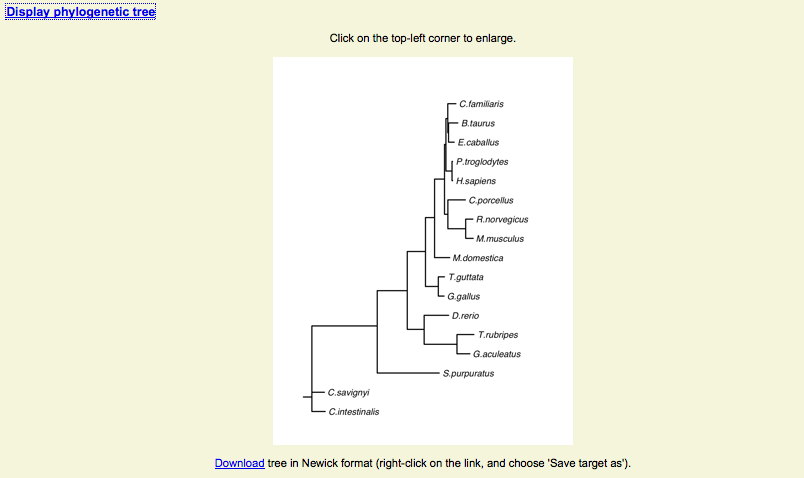
Ortholog analysis - Phylogeny
- A phylogenetic tree has been built for each alignment
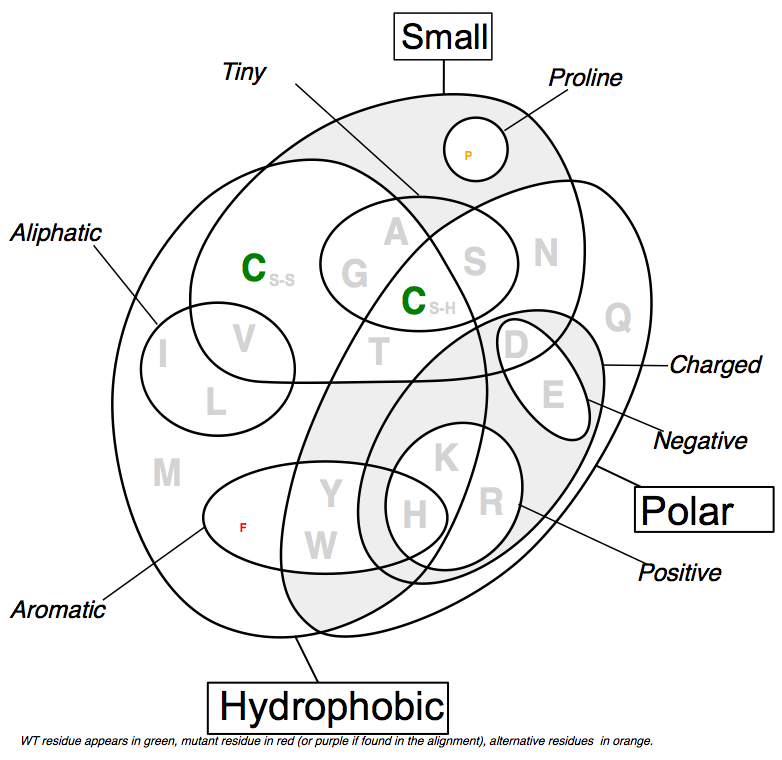
Ortholog/Domain analysis - Venn diagram
- Alternative representation of the alignment at a given position,
- taking physico-chemical properties into account (SVG format)
- Color code
Ortholog/Domain analysis - Venn diagram
- green: wild-type residue
- red: mutant residue not found in the alignment (at the given position)
- purple: mutant residue found in the alignment
- orange: other residues found in the alignment
- grey: other residues not found in the alignment
Ortholog/Domain analysis - Venn diagram
- The size of each letter depends on the representativity of the residue at the position
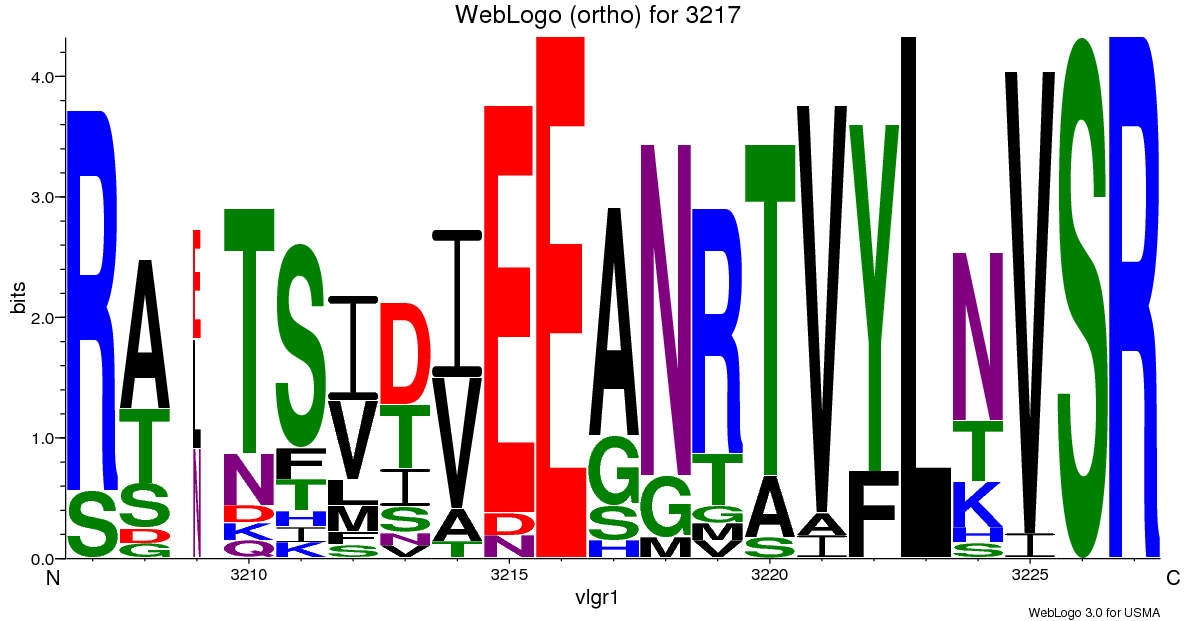
Ortholog/Domain analysis - WebLogos
- WebLogos are also available for the region (21 residues)
Domain analysis - Alignment
- Alignments all come from pfam or prosite
- Include up to 2000 sequences (usherin fnIII)
- Useful to identify structurally crucial residues
- Be careful with less conserved residues, they can have a specific role in your protein!!
Domain analysis - Alignment
- Localization of the domain and summary table of the analysis
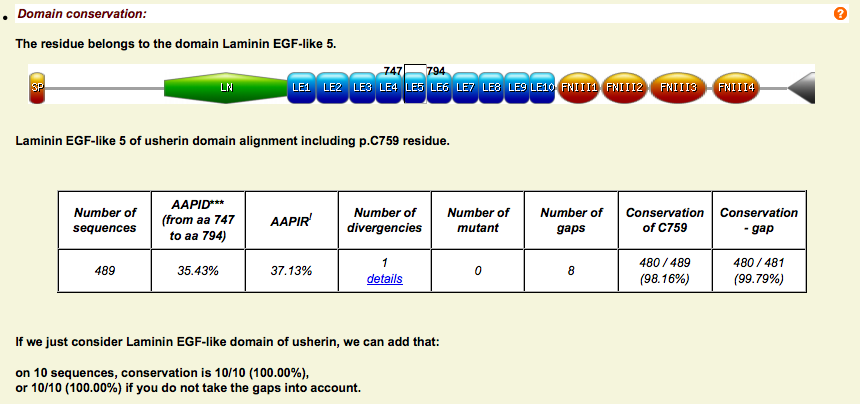
Domain analysis - Alignment
- As for orthologs, real-time svg Venn Diagram and WebLogo
- Possibility to display (clustal format) the complete alignment...
- And therefore to download it for further analysis
Secondary structure - Psipred
- Psipred predictions
- Based on ortholog alignments (better prediction than with a single sequence)
- 3 state prediction: Helix, Strand, Loop
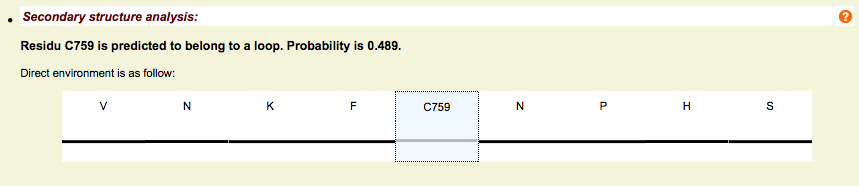
Secondary structure - Frequencies
- Frequencies of observation of each 20 residues in helices and strands...
- Have been estimated based on 8,365 3D structures, representing 1,598,587 residues
- Inclusion:
- non-redundant structures (14,550 structures at first), extracted from the PDB
- Annotated representative structures presenting a resolution < 2.5 Å
Secondary structure - Frequencies
- Exclusion:
- Helices of less or equal to 3 residues
- Strands of less or equal to 2 residues
- Graphs of these calculations available, mapped with:
- Chou-Fasmann, 1978
- Creighton, 1983
- Costantini, 2006
- Frequencies used to determine wether WT and M residues are favorable or not to their predicted stII
Secondary structure - Frequencies
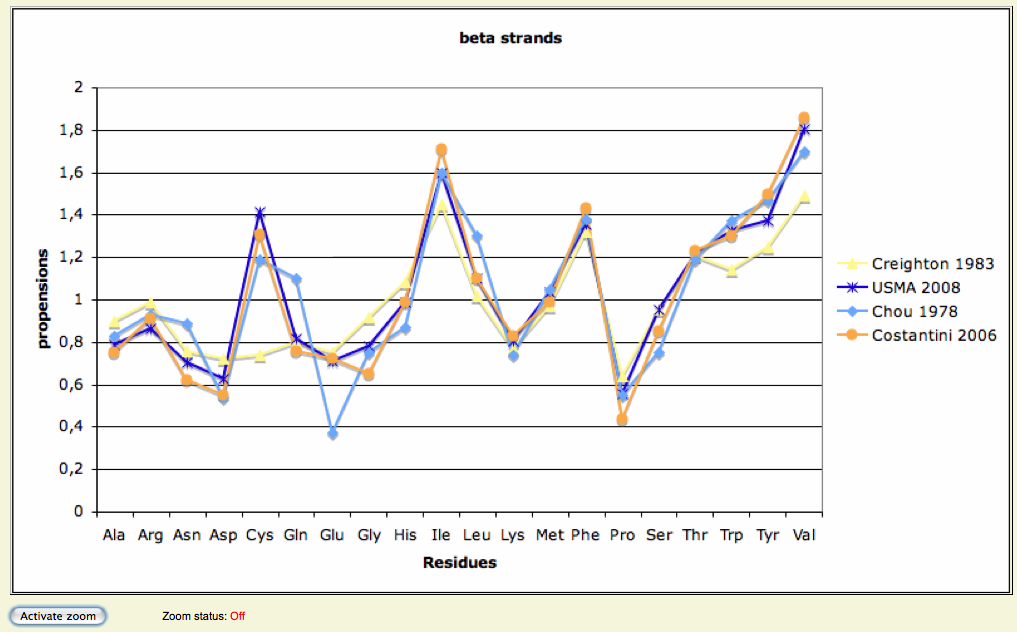
3D analysis - WT structures
USMA is able to analyse 3D structures
- WT structures are "manually" generated, using Domain fishing or @TOME2 for template recognition
- Modeller for model construction
- SCWRL4 for side-chain refinement
- STRIDE for secondary structure assignment
- Molprobity for assessment
- We try to select templates with at least 30% identity (sometimes a little lower)
3D analysis - WT structures
- 3D coverage graphs of each protein are available
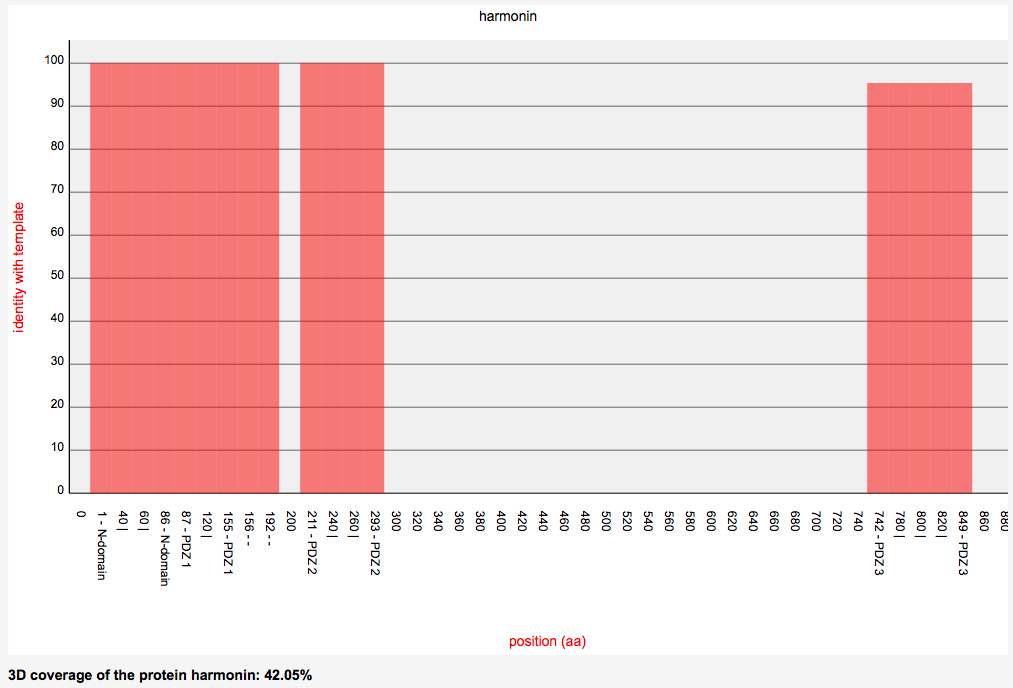
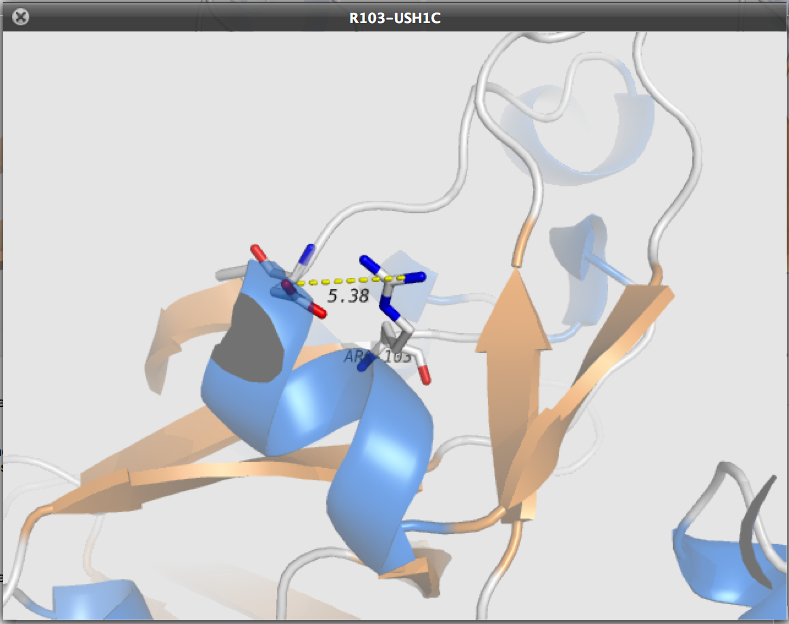
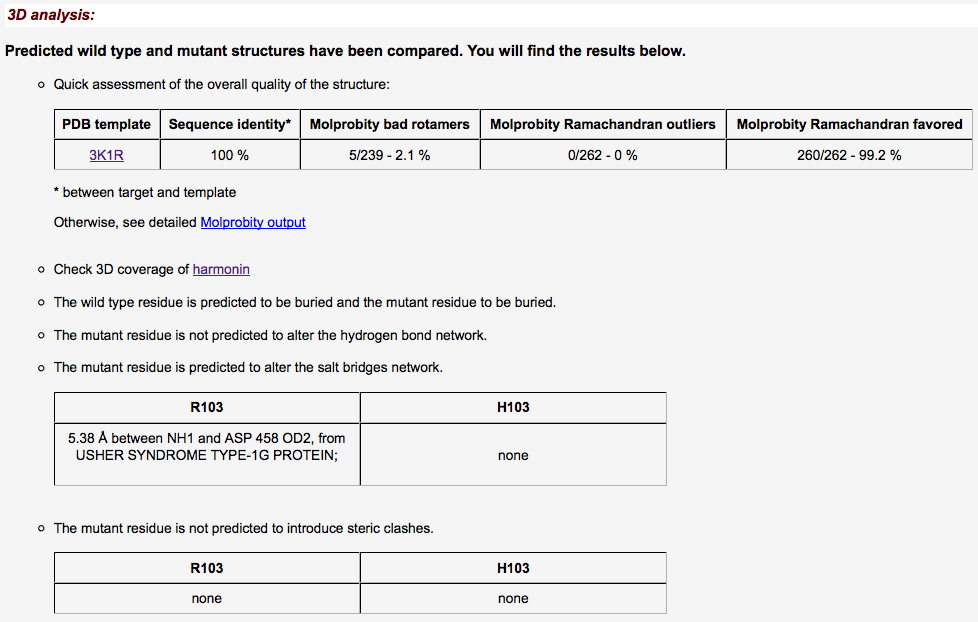
3D analysis - Mutant structures
- USMA generates real-time mutant structures using Modeller
- USMA's "3D engine" computes:
- involvement of wild-type residue
- involvement of mutant residue
- differences
3D analysis
- Involvement means predicted...
- SAS (Solvent Accessibility Surface), computed with msms
- Hydrogen bonds (calulation including distances and bond angles)
- salt bridges network
- disulfide bridges
- steric clashes
3D analysis
USMA also interprets secondary structures features such as amino acids propensities for specific N-Cap, N1-3, interior, C3-C1 and C-Cap positions of α helices and i,i+3 and i,i+4 possible interactions
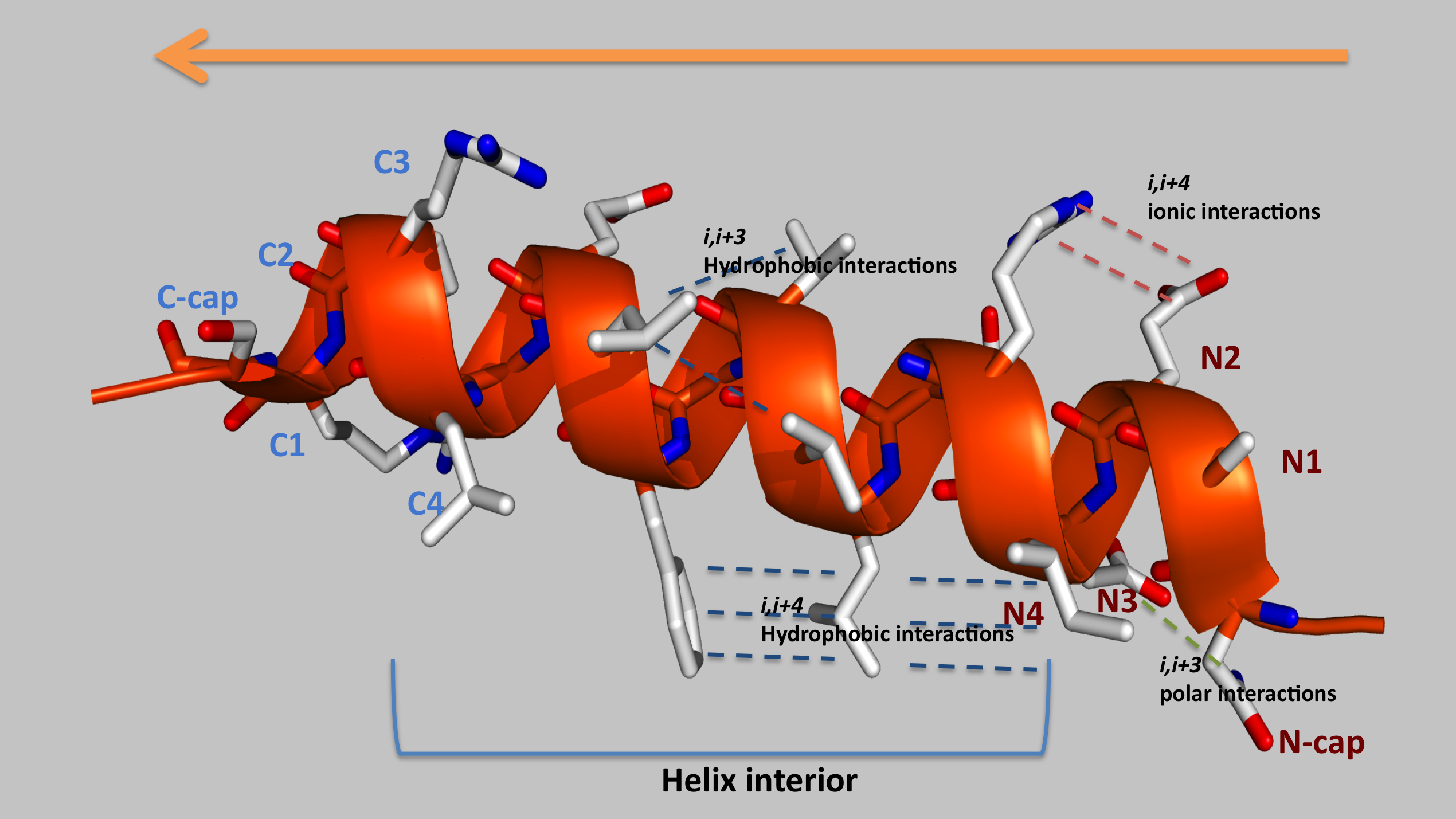
3D analysis
- Results are rendered as a summary table...
3D analysis
- But also 2 fully functional Jmol Applets
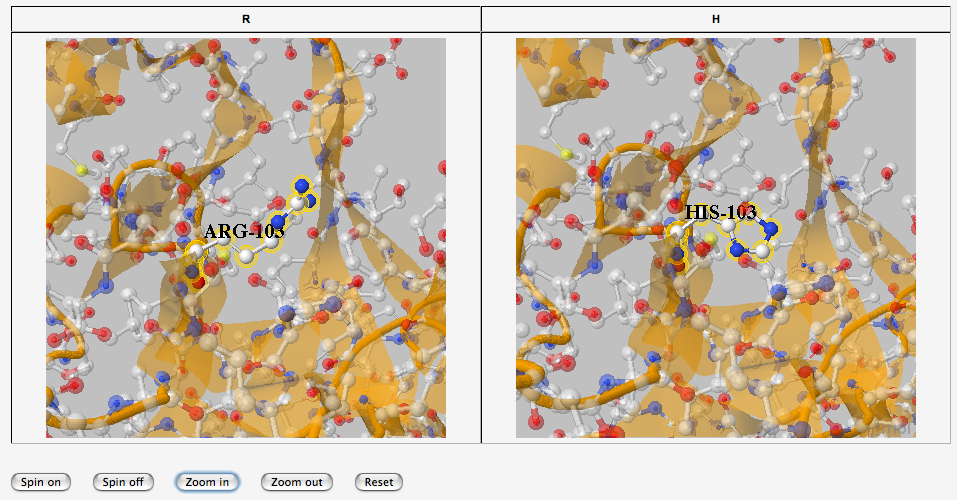
Then the user can perform its own analysis of the models
Additional ressources
- In addition, USMA provides several information:
- UNIPROT annotations concerning the variant if available
- Direct link to LOVD-USHbases
- link to NCBI's graphical view of the region
Last slide
- USMA's just in silico!
- Do not forget other sources
- DNA controls, familial segregation, splicing, and, of course,
- LOVD-USHbases
- Thank you!!
[any material that should appear in print but not on the slide]